Migration assessment TECH PREVIEW
The Voyager Migration Assessment feature is specifically designed to optimize the database migration process from various source databases, currently supporting PostgreSQL and Oracle to YugabyteDB. Voyager conducts a detailed analysis of the source database by capturing essential metadata and metrics. It generates a comprehensive assessment report that recommends effective migration strategies, and provides key insights on ideal cluster configurations for optimal performance with YugabyteDB.
Overview
When you run an assessment, Voyager collects metadata or metrics from the source database. This includes table columns metadata, sizes of tables and indexes, read and write IOPS for tables and indexes, and so on. With this data, Voyager generates an assessment report with the following key details:
-
Database compatibility. An assessment of the compatibility of the source database with YugabyteDB, identifying unsupported features and data types.
-
Cluster size evaluation. Estimated resource requirements for the target environment, to help with planning and scaling your infrastructure. The sizing logic depends on various factors such as the size and number of tables in the source database, as well as the throughput requirements (read/write IOPS).
-
Schema evaluation. Reviews the database schema to suggest effective sharding strategies for tables and indexes.
-
Performance metrics. Voyager analyzes performance metrics to understand workload characteristics and provide recommendations for optimization in YugabyteDB.
-
Migration time estimate. An estimate of the time needed to import data into YugabyteDB after export from the source database. These estimates are calculated based on various experiments during data import to YugabyteDB.
Caveat
The recommendations are based on testing using a RF3 YugabyteDB cluster on instance types with 4GiB memory per core and running v2024.1.Note that if providing database access to the client machine running Voyager is not possible, you can gather metadata from the source database using the provided bash scripts and then use Voyager to assess the migration.
The following table describes the type of data that is collected during a migration assessment.
| Data | Collected | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Application or user data | No | No application or user data is collected. |
| Passwords | No | The assessment does not store any passwords. |
| Database metadata schema, object, object names |
Yes | Voyager collects the schema metadata including table IOPS, table size, and so on, and the actual schema. |
| Database name | Yes | Voyager collects database and schema names to be used in the generated report. |
| Performance metrics | Optional | Voyager captures performance metrics from the database (IOPS) for rightsizing the target environment. |
| Server or database credentials | No | No server or database credentials are collected. |
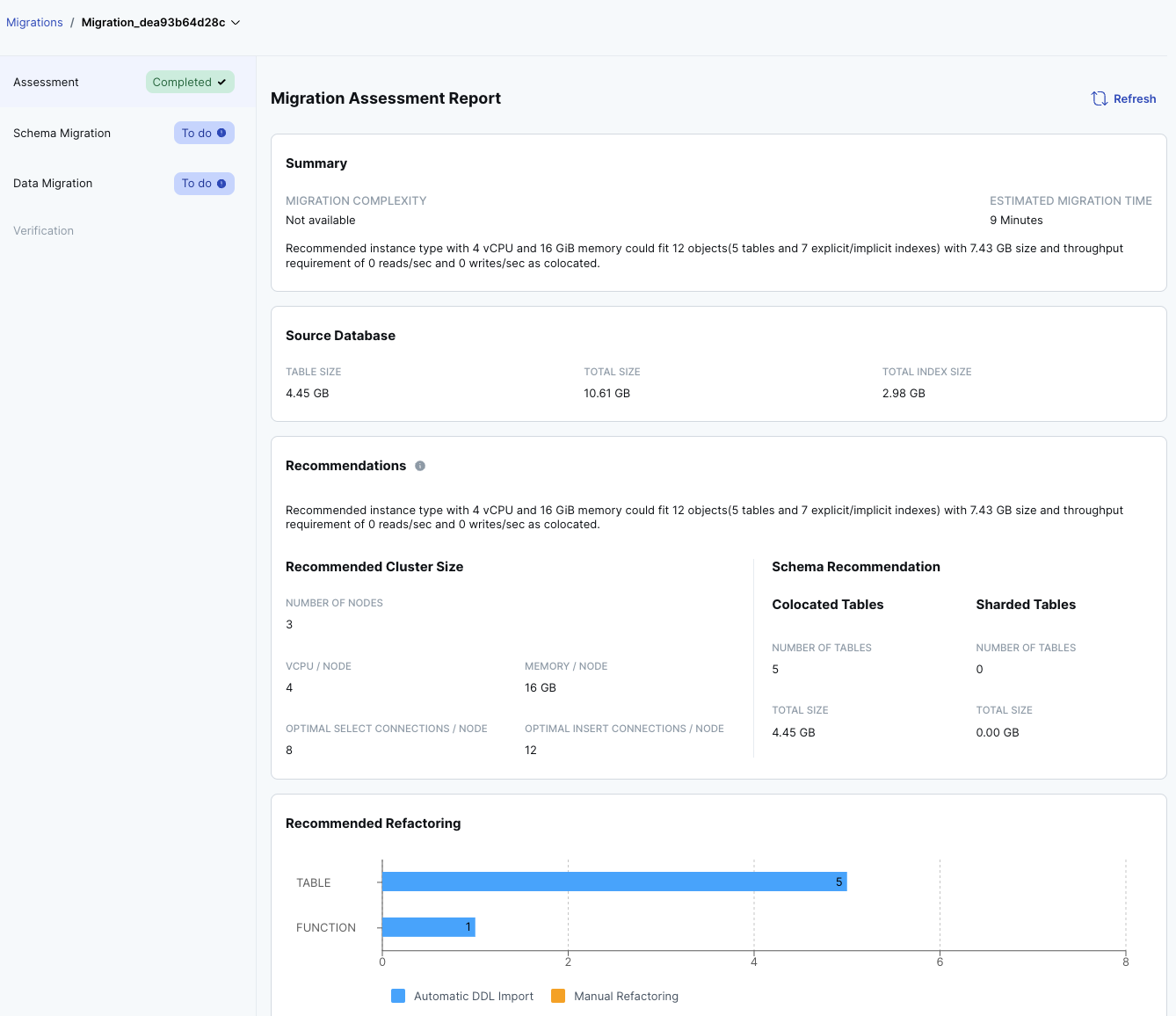
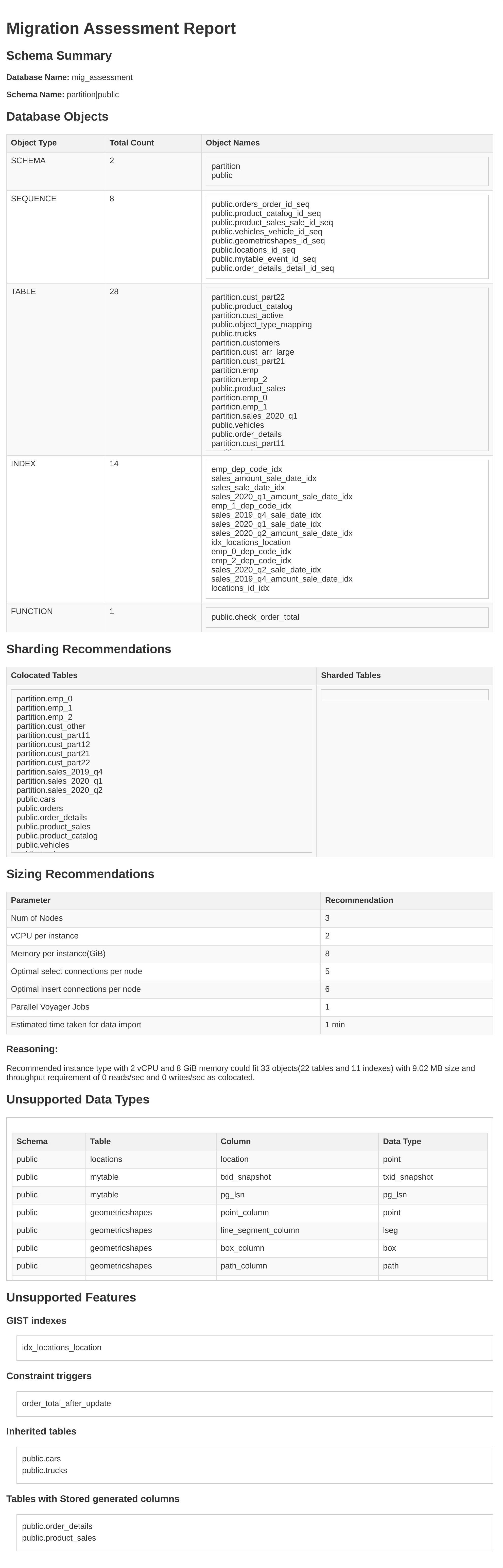
PostgreSQL Sample Migration Assessment report
A sample Migration Assessment report for PostgreSQL is as follows:
Generate a Migration Assessment report
-
Prepare the source database.
-
Create a new user,
ybvoyageras follows:CREATE USER ybvoyager PASSWORD 'password'; -
Grant necessary permissions to the
ybvoyageruser./* Switch to the database that you want to migrate.*/ \c <database_name> /* Grant the USAGE permission to the ybvoyager user on all schemas of the database.*/ SELECT 'GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA ' || schema_name || ' TO ybvoyager;' FROM information_schema.schemata; \gexec /* The above SELECT statement generates a list of GRANT USAGE statements which are then executed by psql because of the \gexec switch. The \gexec switch works for PostgreSQL v9.6 and later. For older versions, you'll have to manually execute the GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA schema_name TO ybvoyager statement, for each schema in the source PostgreSQL database. */ /* Grant SELECT permission on all the tables. */ SELECT 'GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA ' || schema_name || ' TO ybvoyager;' FROM information_schema.schemata; \gexec
-
Create a role that has the privileges as listed in the following table:
Permission Object type in the source schema SELECTVIEW, SEQUENCE, TABLE PARTITION, TABLE, SYNONYM, MATERIALIZED VIEW EXECUTETYPE Change the
<SCHEMA_NAME>appropriately in the following snippets, and run the following steps as a privileged user.CREATE ROLE <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role; BEGIN FOR R IN (SELECT owner, object_name FROM all_objects WHERE owner=UPPER('<SCHEMA_NAME>') and object_type in ('VIEW','SEQUENCE','TABLE PARTITION','SYNONYM','MATERIALIZED VIEW')) LOOP EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'grant select on '||R.owner||'."'||R.object_name||'" to <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role'; END LOOP; END; / BEGIN FOR R IN (SELECT owner, object_name FROM all_objects WHERE owner=UPPER('<SCHEMA_NAME>') and object_type ='TABLE' MINUS SELECT owner, table_name from all_nested_tables where owner = UPPER('<SCHEMA_NAME>')) LOOP EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'grant select on '||R.owner||'."'||R.object_name||'" to <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role'; END LOOP; END; / BEGIN FOR R IN (SELECT owner, object_name FROM all_objects WHERE owner=UPPER('<SCHEMA_NAME>') and object_type = 'TYPE') LOOP EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'grant execute on '||R.owner||'."'||R.object_name||'" to <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role'; END LOOP; END; / GRANT SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE TO <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role; GRANT SELECT ANY DICTIONARY TO <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role; GRANT SELECT ON SYS.ARGUMENT$ TO <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role; -
Create a user
ybvoyagerand grantCONNECTand<SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_roleto the user:CREATE USER ybvoyager IDENTIFIED BY password; GRANT CONNECT TO ybvoyager; GRANT <SCHEMA_NAME>_reader_role TO ybvoyager;
-
-
Assess migration - Voyager supports two primary modes for conducting migration assessments, depending on your access to the source database as follows:
-
With source database connectivity: This mode requires direct connectivity to the source database from the client machine where voyager is installed. You initiate the assessment by executing the
assess-migrationcommand ofyb-voyager. This command facilitates a live analysis by interacting directly with the source database, to gather metadata required for assessment. A sample command is as follows:yb-voyager assess-migration --source-db-type postgresql \ --source-db-host hostname --source-db-user ybvoyager \ --source-db-password password --source-db-name dbname \ --source-db-schema schema1,schema2 --export-dir /path/to/export/dir -
Without source database connectivity (only PostgreSQL): In situations where direct access to the source database is restricted, there is an alternative approach. Voyager includes packages with scripts for PostgreSQL at
/etc/yb-voyager/gather-assessment-metadata. You can perform the following steps with these scripts:-
On a machine which has access to the source database, copy the scripts and install dependencies psql, and pg_dump version 14 or later. Alternatively, you can install yb-voyager on the machine to automatically get the dependencies.
-
Run the
yb-voyager-pg-gather-assessment-metadata.shscript by providing the source connection string, the schema names, path to a directory where metadata will be saved, and an optional argument of an interval to capture the IOPS metadata of the source (in seconds with a default value of 120). For example,/path/to/yb-voyager-pg-gather-assessment-metadata.sh 'postgresql://ybvoyager@host:port/dbname' 'schema1|schema2' '/path/to/assessment_metadata_dir' '60' -
Copy the metadata directory to the client machine on which voyager is installed, and run the
assess-migrationcommand by specifying the path to the metadata directory as follows:yb-voyager assess-migration --source-db-type postgresql \ --assessment-metadata-dir /path/to/assessment_metadata_dir --export-dir /path/to/export/dir
The output of both the methods is a migration assessment report, and its path is printed on the console.
-
Important
For the most accurate migration assessment, the source database must be actively handling its typical workloads at the time the metadata is gathered. This ensures that the recommendations for sharding strategies and cluster sizing are well-aligned with the database's real-world performance and operational needs. -
-
Create a target YugabyteDB cluster as follows:
-
Create a cluster in Enhanced Postgres Compatibility Mode based on the sizing recommendations in the assessment report. For a universe in YugabyteDB Anywhere, enable the compatibility mode by setting some flags on the universe.
-
Create a database with colocation set to TRUE.
CREATE DATABASE <TARGET_DB_NAME> with COLOCATION=TRUE;
-
-
Proceed with migration with one of the migration workflows:
Visualize the Migration Assessment report
yugabyted UI allows you to visualize the database migrations performed by YugabyteDB Voyager. The UI provides details of migration complexity, SQL objects details from the source database, YugabyteDB sharding strategy, conversion issues (if any), and also allows you to track the percentage completion of data export from the source database and data import to the target YugabyteDB cluster.
Prerequisites
Before you begin the Voyager migration, do the following:
-
Start a local YugabyteDB cluster using the steps described in Use a local cluster section.
Send Voyager details to a local YugabyteDB cluster
Set the following environment variables before starting the migration:
export CONTROL_PLANE_TYPE=yugabyted
export YUGABYTED_DB_CONN_STRING=<ysql-connection-string-to-yugabyted-instance>
For example, postgresql://yugabyte:yugabyte@127.0.0.1:5433
Assess Migration
Voyager Migration Assessment conducts a detailed analysis of the source database by capturing essential metadata and metrics. Yugabyted UI allows you to go over the assessment report which includes recommendations of effective migration strategies, migration complexity, and provides an overview on effort involved in migrating from the source database.
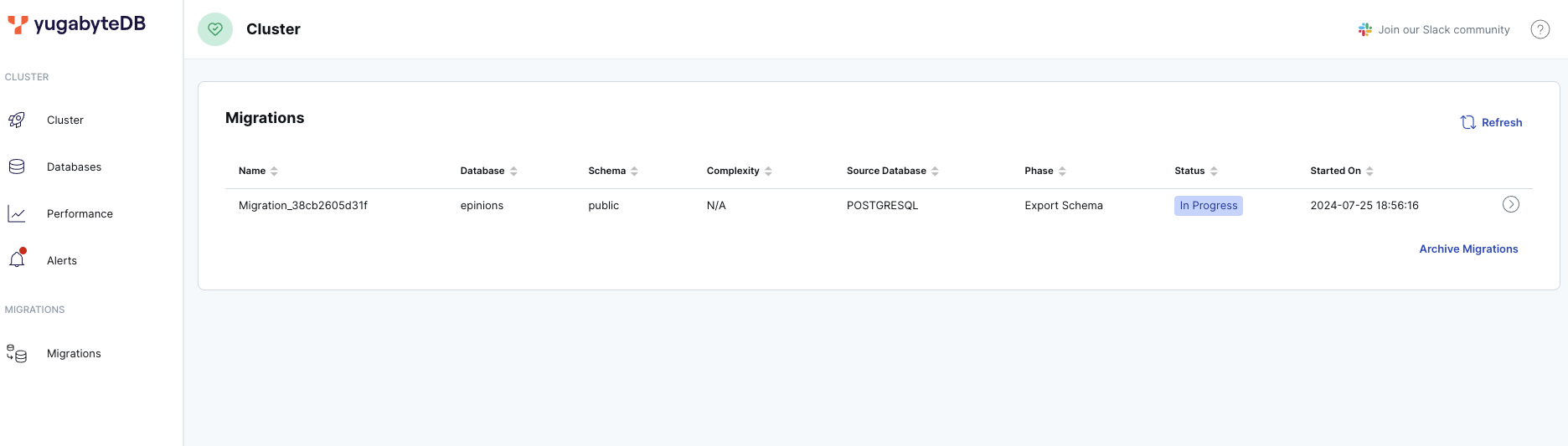
After generating a Migration Assessment Report, from yugabyted UI, navigate to Migrations tab, available at http://127.0.0.1:15433 to see a list of the available migrations.
Migrations
Migration Assessment UI